Abstract:
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VaD) are progressive neurodegenerative conditions characterized by functional impairment and reduced quality of life. Despite extensive research, effective treatments for these conditions remain elusive. While pharmacological interventions (Ps) like cholinesterase inhibitors are common, their impact on disease progression is minimal. Non- pharmacological interventions (NPI), including computerised cognitive training (CCT) and cognitive stimulation therapy (CST), have gained attention as potential adjunctive therapies. However, the comparative effectiveness of NPIs to Pls remains unclear.
Methods: This meta-analysis was performed according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses) guidelines 2020, and the review protocol was registered in PROSPERO (Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews) CRD42024590061. Databases like PUBMED, Google Scholar, and COCHRANE Library were hand-searched for CTs. A systematic search using MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) was done. Covidence software was used for screening, selection of articles and data extraction. Heterogeneity among the studies was examined using the Higgins 12 test, where 12 < 25% is considered to be low risk, ≥ 50% as moderate risk, and ≥ 75% as high risk. Random-effect models were used for the meta- analysis as I2 values were ≥ 50%. Quality assessment and risk of bias were assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool.
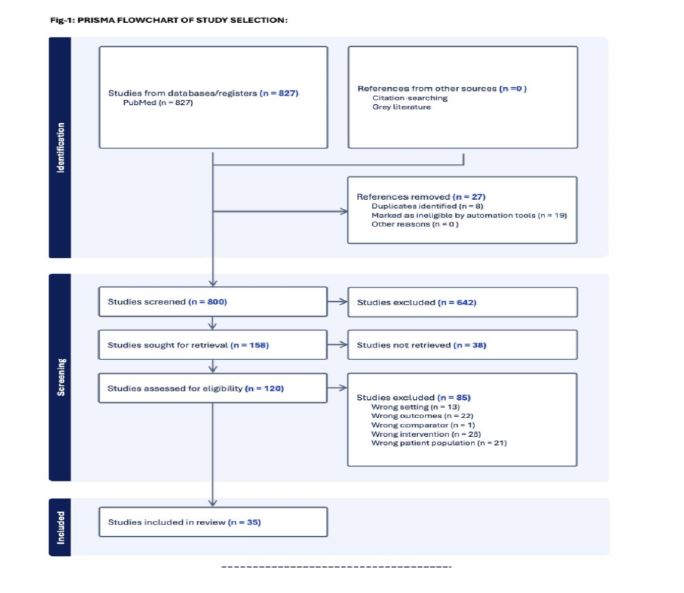
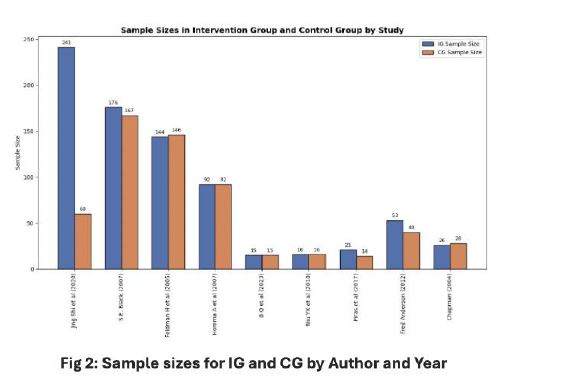
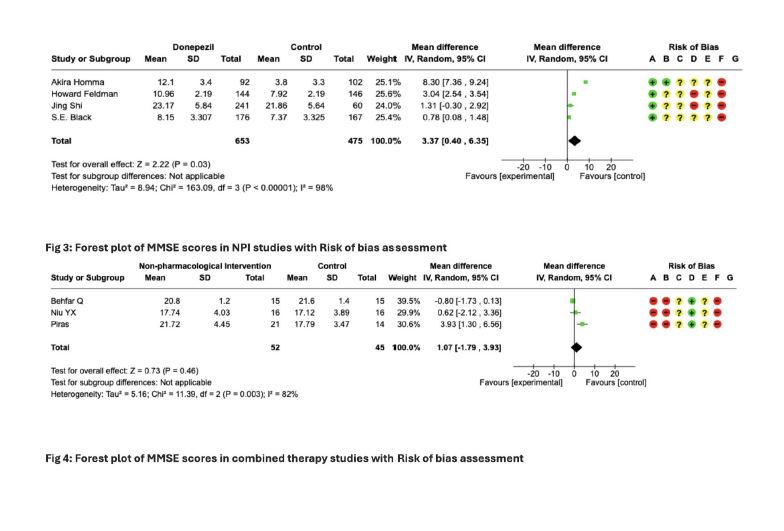
Results: A total of 2,426 studies were identified, which were screened for full-text, and 827 studies were screened to fit the selection criteria. Thirty-five studies that met the selection criteria were taken for qualitative synthesis. Four different outcomes were measured using standard scales, respectively. We found that Donepezil had a significant positive effect on the cognitive function of patients with both AD and VaD (MD=3.37, 95% C1:0.40, 6.35, p<0.05).
Conclusion: MMSE scores were assessed for all the studies (n= 1,372) before and after the intervention. MMSE scores in studies analyzing the effectiveness of Pls (n= 1,128) in patients with AD and VaD showed statistically significant improvement in cognitive outcomes in IG. Hence use of DONEPEZIL proves to have promising effects in improving patient outcomes. NPIs are particularly effective for patients with mild disease. In contrast. Pls tend to show more benefits in moderate to severe disease.
Biography:
He is a final-year medical student with a focused research interest in neurodegenerative disorders. He is an ICMR-STS Scholar and a grant awardee for research on HFLC and its association with platelet parameters in dengue, runner-up at a medical symposium for research conducted with the Alzheimer’s and Related Disorders Society of India. He was a MedSRT internee at the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Hyderabad, Secretary and Editor-in-Chief at my college research club, and an organising member of OSMECON 2023 and received awards for neurology-focused research at UG conferences. He is a member of ISTAART, GNA & AAN, certified in systematic review and meta-analysis from Johns Hopkins.
Copyright 2024 Mathews International LLC All Rights Reserved